In the field of surveying and geospatial engineering, precision is non-negotiable. Whether establishing primary control points for large-scale infrastructure or performing geodetic mapping in remote or complex terrain, high-precision GNSS techniques are essential.
Among these, static GNSS surveying continues to stand out for its reliability and sub-centimeter accuracy. Using industry standards and field-proven workflows, we will examine the continued importance of static GNSS in an era increasingly dominated by real-time technologies such as Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) and Post-Processed Kinematic (PPK). You will leave with a clear understanding of how static GNSS works, how it differs from dynamic positioning, and how it can be seamlessly integrated into your surveying workflow.
Foundations of GNSS and Static Measurements
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) refers to satellite constellations such as GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), QZSS (Japan), and BeiDou (China). These systems transmit radio signals that allow ground-based receivers to calculate their position by measuring the signal propagation time from multiple satellites.
However, raw GNSS signals are affected by several sources of error, including ionospheric and tropospheric delays, satellite clock and orbit inaccuracies, and multipath interference. These factors can significantly degrade positioning accuracy. This is where static GNSS positioning becomes essential. In this method, a receiver is placed at a fixed location for an extended period - typically 15 minutes to several hours - to collect high-quality raw signal data. The longer observation time helps to average out random errors and resolve carrier phase ambiguities, enabling millimeter-level accuracy.

Static positioning is ideal for applications such as geodetic control, permanent station installation, and reference network densification. CHCNAV's i93 and iBase receivers support multi-frequency tracking and integrate seamlessly with CGO2.0 post-processing software, enabling surveyors to calculate high-precision coordinates even in challenging environments.
Why Do We Still Need Static Measurements?
Static GNSS measurements are far more than a fallback -they remain the preferred method for applications requiring maximum precision and data reliability. By collecting extended observational data, static techniques are uniquely capable of mitigating issues such as satellite geometry fluctuations, atmospheric disturbances, and multipath interference.
- High-Precision Control for Critical Projects: in high-stakes scenarios -such as infrastructure development, boundary demarcation, or primary control network establishment- even centimeter-level errors can lead to costly misalignments. Static GNSS enables millimeter-level accuracy through long observation sessions that average out noise and resolve carrier-phase ambiguities. When aligning control points with a national geodetic datum, static observations ensure coordinate consistency and repeatability.
- Reliable Control Point Verification and Densification: Control points may shift over time due to environmental changes or crustal movement, particularly in seismically active regions. Static GNSS allows surveyors to reoccupy and revalidate these points with high accuracy, and to introduce new intermediate stations to densify networks, ensuring spatial continuity and minimizing error propagation in large-scale projects.
- Long-Term Stability: Static GNSS offers unmatched long-term measurement stability. Unlike real-time solutions, which can degrade due to temporary signal obstructions or atmospheric anomalies, static techniques maintain performance in all conditions. This makes them ideal for permanent base stations and deformation monitoring networks.
- Performance in Challenging Environments: In locations with poor GNSS visibility such as urban canyons, dense forests, or mountainous terrain, static methods excel. A stationary receiver can track partial signals continuously, and extended observation time enables advanced error correction during post-processing. CHCNAV receivers, featuring robust signal tracking and interference mitigation algorithms, are specifically designed for these environments, ensuring data completeness and positional accuracy.
How Do Static Measurements Work?
Static GNSS surveying is a systematic method designed to achieve maximum positional accuracy through long-duration signal tracking and advanced post-processing techniques. The process consists of three key phases:
- Setup and Observation: The procedure begins by placing two or more GNSS receivers at fixed positions, one at a known reference point (base station), and the others at unknown locations (rovers or survey stations). These receivers must remain stationary and simultaneously track signals from at least four common satellites. In many cases, data from Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) or national geodetic networks can be used as the base input, reducing the need to deploy extra hardware in the field.
- Data Collection: Each receiver records raw GNSS observables, with an emphasis on carrier-phase data, which captures the signal’s wave cycles at a high resolution. This data is essential for resolving integer ambiguities, a key step in achieving sub-centimeter accuracy. Observation duration depends on factors such as baseline length, satellite visibility, and signal quality. For baselines under 10 km, a session of 15 to 30 minutes is often sufficient. Longer baselines over 30 km, or environments with high interference, may require several hours or even days of data collection to ensure reliable results.
- Post-Processing: After data collection, the raw files are imported into post-processing software, such as CHCNAV’s CGO, for precise coordinate computation. The software calculates the baseline vector between reference and rover stations and corrects for satellite orbit errors, atmospheric delays, and clock discrepancies using precise ephemeris data and correction models. A key advantage of CGO2.0 is its automated workflow: it simplifies ambiguity resolution, performs statistical quality checks, and adjusts network geometry when multiple stations are involved. The final output is a high-precision positioning solution, complete with accuracy metrics, which can be exported in various coordinate systems to match project specifications.
CHCNAV CGO Post processing software
Differences Between Static GNSS, RTK, and PPK
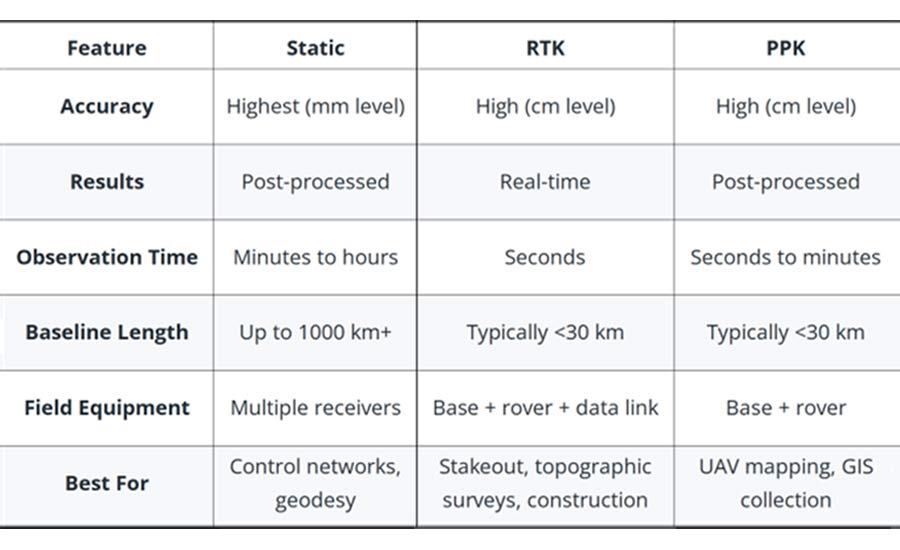
Choosing the right GNSS correction method is imperative to meet your surveying requirements. Static GNSS, RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) and PPK (Post-Processed Kinematic) each offer different strengths in terms of accuracy, workflow and environmental suitability.

CHCNAV iBase GNSS receiver
- Static GNSS provides the highest positional accuracy, often achieving millimeter-level precision for foundational work. It requires stationary data collection over extended periods and relies on post-processing to eliminate errors. This method is ideal for control network establishment, geodetic baseline creation, long-distance measurements and projects where absolute reliability and repeatability are critical.
- GNSS RTK supports real-time positioning where a base station transmits live correction data to a rover via radio or cellular networks. It provides centimeter-level accuracy while the rover is moving, making it ideal for construction stakeouts, topographic surveys, and machine control systems. However, RTK has limitations because it requires a stable communication link and works best over short baselines (typically <30 km). Accuracy can also be degraded by signal dropouts, limited satellite visibility, or atmospheric variability.
- GNSS PPK combines post-processing accuracy with mobile data collection. It is well suited for UAVs, vehicle-mounted surveys, and other applications where the rover is constantly in motion. After fieldwork, GNSS data is synchronized with a base station and corrected post-mission, eliminating the need for a live data link. It typically achieves sub-decimeter to centimeter accuracy. While more accurate than RTK in unstable environments, PPK typically does not achieve the millimeter-level accuracy of static GNSS, especially over long baselines or in difficult terrain.
How to Implement Static Measurements in Your Projects
The key to successful static GNSS workflows is pairing GNSS raw data collection with reliable office processing. CHCNAV’s LandStar and CGO software solutions streamline the entire process, from data capture to final coordinate output. These solutions support tasks such as baseline computation, loop closure analysis, and network adjustment.
Field Setup with CHCNAV LandStar : LandStar offers a user-friendly interface for configuring static GNSS data collection. Users can define essential parameters such as RINEX format, logging rate (e.g., 1 Hz), antenna height (slant or vertical), and session duration. Tools such as elevation mask settings and others options help optimize data quality. Once configured, the system records raw satellite data ready for post-processing and can be used for accurate baseline and network analysis.
Post-Processing with CHCNAV CGO : CGO is CHCNAV’s dedicated office software for processing GNSS observations. It guides users through importing raw data, computing baselines, and performing network adjustments using least-squares methods. Built-in tools allow for loop closure validation, residual analysis, and coordinate export. With support for RINEX files, multiple base stations, and robust quality control, CGO ensures a structured and reliable workflow for geodetic, cadastral, and engineering projects that require high positioning accuracy.
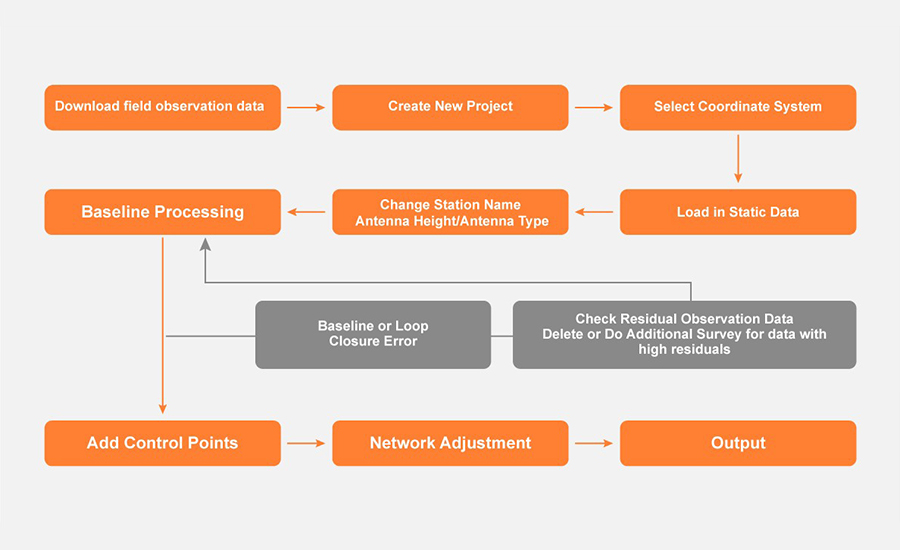
GNSS data post-processing workflow
The Enduring Value of Static GNSS in a Dynamic Surveying World
Static GNSS surveying remains the gold standard for high-precision geodetic applications, delivering unmatched accuracy, long-term reliability and strong performance in complex environments. While RTK offers real-time convenience and PPK adds flexibility for mobile workflows, static methods remain essential for establishing control networks, validating geospatial data, and ensuring consistency in large-scale surveying and engineering projects.
CHCNAV's integrated static GNSS solutions - from advanced dual-frequency receivers like the CHCNAV i93 Series to powerful post-processing platforms like CHCNAV CGO 2.0 - enable professionals to streamline workflows from the field to the office without compromising scientific rigor. From mountainous regions and urban canyons to infrastructure projects and national geodetic networks, static measurements ensure that every fundamental coordinate is backed by precision and integrity.
For surveyors, engineers and geospatial professionals looking to future-proof their positioning strategies, investing in robust static GNSS capabilities is not just an advantage, it is essential. Discover how CHCNAV's technology can raise your accuracy standards and contact our experts for customized support on your next project.
____
About CHC Navigation
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) develops advanced mapping, navigation and positioning solutions designed to increase productivity and efficiency. Serving industries such as geospatial, agriculture, construction and autonomy, CHCNAV delivers innovative technologies that empower professionals and drive industry advancement. With a global presence spanning over 140 countries and a team of more than 2,000 professionals, CHC Navigation is recognized as a leader in the geospatial industry and beyond. For more information about CHC Navigation [Huace:300627.SZ], please visit: www.chcnav.com






.png)

