INTRODUCTION TO LIDAR IN MINING
Open-pit mining, a fundamental method of extracting valuable minerals from the earth, faces numerous operational challenges, including maintaining efficiency and ensuring site safety. In this complex environment, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology is emerging as a transformative tool. LiDAR's ability to generate precise, three-dimensional information about the earth's surface and the objects on it significantly enhances mining operations. This technology offers a leap in accuracy and efficiency, providing a detailed analysis of the mining environment that traditional methods cannot match.
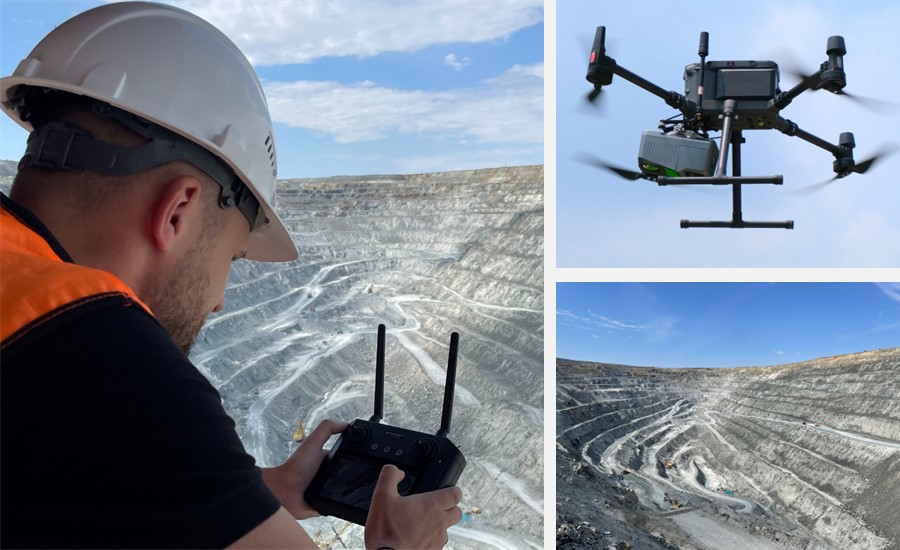

Figure 1. UAV-based LiDAR survey of an open-pit mine.
THE ESSENTIAL ROLE OF SURVEYORS IN OPEN-PIT MINING
Surveying in open pit mining is of vital importance. It encompasses a range of tasks that are critical to the operational success and safety of mining operations. Surveyors are tasked with accurately placing explosives, dynamically mapping the terrain, and accurately estimating the volume of material being mined. Traditional methods, while effective to a point, often fall short of the required levels of accuracy and efficiency.
- Optimizing explosive placement: Precise placement of explosives is critical for effective rock fragmentation, which in turn increases the efficiency of mineral extraction.
- Dynamic terrain mapping: Constantly updated terrain maps are essential for navigating the ever-changing landscape of a mine, ensuring that mining operations are based on the most up-to-date data.
- Accurate volume estimates: Accurately determining the volume of excavated material, extracted minerals, and stockpiles is fundamental to operational planning and financial forecasting.
CHALLENGES WITH CONVENTIONAL SURVEYING TECHNIQUES
While traditional surveying techniques have been the foundation for decades, they have limitations. These include compromised accuracy due to the manual nature of the tasks, operational delays due to time-consuming processes, and increased risk to survey personnel who must navigate hazardous environments.
- Compromised accuracy: The complex nature of mine topography, combined with the irregular shapes of materials, often results in volume measurement inaccuracies.
- Operational delays: Manual data collection in challenging terrain is time-consuming, impacting the ability to make real-time decisions.
- Increased risk: The inherent risks of the mining environment (steep slopes, falling rocks, and unstable formations …) pose a significant safety threat to survey personnel.
THE TRANSFORMATION THROUGH LIDAR TECHNOLOGY
LiDAR technology addresses these challenges head-on. Its efficiency and accuracy surpass traditional surveying methods, significantly reducing operational delays and improving safety. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with LiDAR systems can quickly scan large areas, providing real-time data critical for informed decision-making. This capability not only speeds up the surveying process but also minimizes risk to personnel by reducing the need for an on-the-ground presence in potentially dangerous areas.
- Increased efficiency: LiDAR-equipped UAVs capture millions of precise data points per second, creating detailed 3D models of mine sites. This method significantly outperforms traditional surveying techniques, covering large areas quickly and with fewer personnel, streamlining survey operations, and reducing time and labor costs.
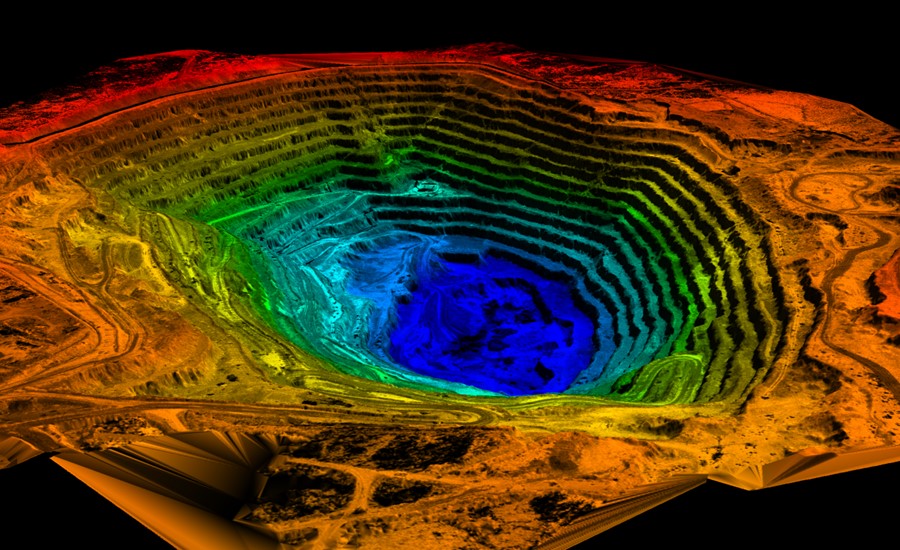
Figure 2. Digital elevation model (DEM) of open pit mine.
- Unmatched accuracy: LiDAR provides detailed, high-resolution data that enables more informed and accurate decision-making. By creating highly accurate 3D models, LiDAR enables precise volume calculations, stockpile measurements, and slope analysis.
- Improved safety: One of the most important advances of LiDAR is its contribution to surveyor safety. Traditional surveying often places personnel near hazardous conditions, such as active blasting zones or unstable terrain. By minimizing the need for human presence in hazardous areas, airborne LiDAR survey significantly improves safety conditions for survey crews.
OVERVIEW OF LIDAR-BASED SURVEYING PROCESS
The LiDAR surveying process involves several steps, from initial flight planning to final data processing. LiDAR systems, among them the CHCNAV AlphaUni 20 (AU20), streamline this process. In addition, integration with advanced software solutions enables efficient processing and analysis of LiDAR data, resulting in actionable insights for mining operations.
1. Flight Planning:
- Software assistance: Using software such as CHCNAV's SmartGo or DJI Pilot 2, UAVs are guided through meticulously planned flight paths. This ensures unparalleled coverage and data collection by tailoring flight paths to the unique requirements of each mine site, optimizing both efficiency and safety.
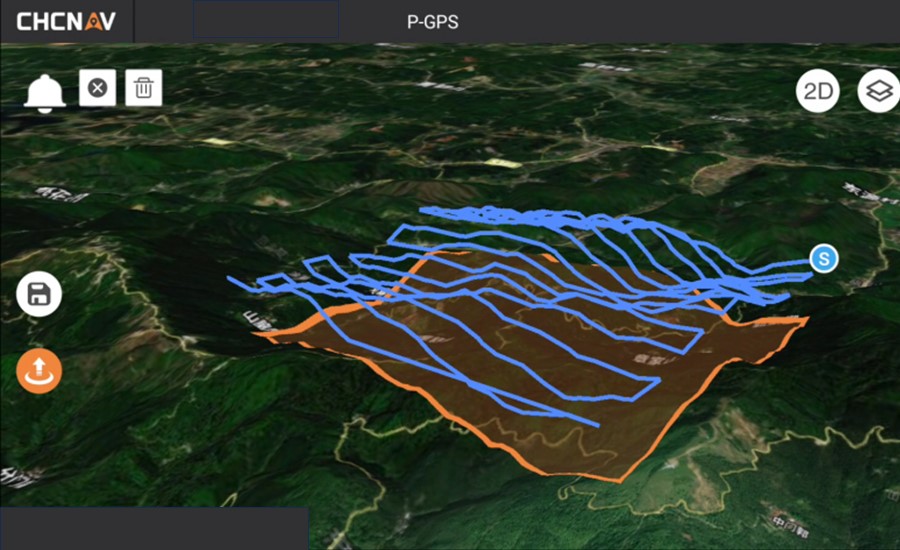
Figure 3. Flight route planning for UAV LiDAR survey.
- GNSS corrections: The accuracy of scanning results depends on LIDAR, UAV positioning accuracy, and data processing. The accuracy of positioning is greatly enhanced by real-time kinematic (RTK) or post-processed kinematic (PPK) corrections. Combined with strategically placed ground control points, these corrections refine the accuracy of the data to the highest level, ensuring that every point acquired contributes to a comprehensive and accurate survey.
2. Data Collection:
- Real-time monitoring: Automation of data collection is complemented by vigilant real-time monitoring for identifying and mitigating potential problems such as lost RTK connections or unexpected interference. In addition, unforeseen challenges, such as denser vegetation than originally anticipated, may require manual intervention by the surveyor to ensure comprehensive coverage and data integrity. This adaptive approach ensures the highest quality of data collection and that no detail is missed.
3. Data Processing:
- Software integration: LiDAR data's journey from raw points to actionable insights begins with its import into advanced processing software, such as CHCNAV's CoPre Software. Here, the data undergoes a meticulous sequence of filtering, correction, classification, and finally, modeling into formats such as Digital Elevation Models (DEM) in the CoProcess software. This transformative process refines the raw data into a structured and highly usable form, ready for in-depth analysis and application in mining operations.
4. Data Application:
The CHCNAV's sophisticated CoProcess software provides unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in modeling and analysis.
- Volume calculations: CoProcess enables accurate determination of the volume of material extracted over specific time periods, improving production monitoring and resource management.
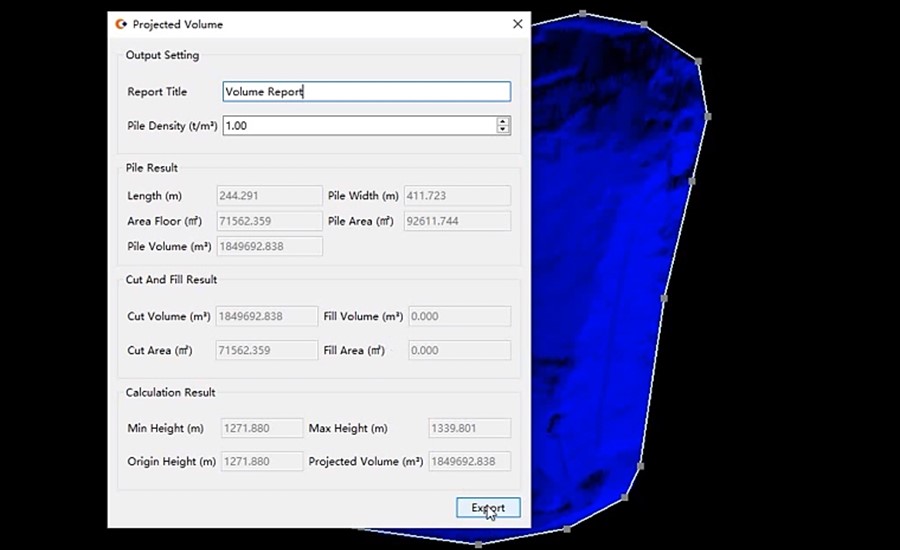
Figure 4. The calculation of the volume of material extracted over specific time periods in the CoProcess software.
- Stockpile analysis: CoProcess efficiently calculates the height, area and volume of stockpiles, facilitating inventory management and logistics planning.

Figure 5. Stockpile analysis in the Coprocess software.
- Slope analysis: Using LiDAR data, CoProcess software automates the extraction of key slope metrics such as top and bottom edges and slope angles. This information can be seamlessly exported in DLG format for easy integration with CAD software. Conducting thorough slope stability assessments and formulating effective risk mitigation strategies increases the safety and operational efficiency of open-pit mining projects.
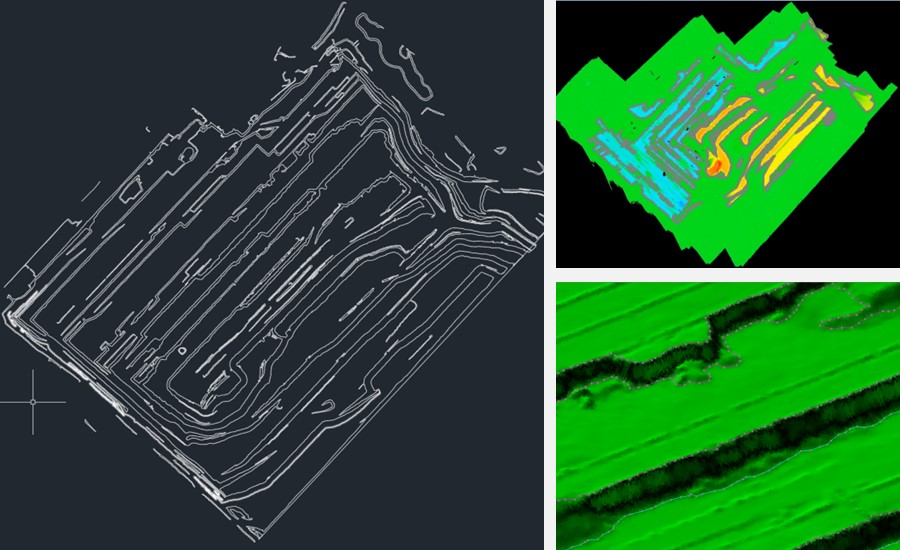
Figure 6. Slope lines data generation and analysis in CoProcess software.
CRITERIA FOR SELECTING THE RIGHT LIDAR SYSTEM
Selecting the right LiDAR system for an open-pit mine requires the evaluation of several factors. The ideal system should offer a comprehensive ecosystem that integrates seamlessly with existing operations, robust scanning capabilities to capture detailed terrain data, and cost-effectiveness to ensure a high return on investment. CHCNAV's AlphaUni 20 (AU20) stands out as a system that meets these criteria, offering a blend of high accuracy, operational flexibility and ease of use, making it a top choice for mining surveyors.
- Comprehensive ecosystem: Essential for streamlined operations, it includes compatible sensors, UAV platforms, and both flight planning and post-processing software. CHCNAV’s solutions provide a fully integrated ecosystem, ensuring compatibility and efficient workflow throughout the survey process.
- Scanning capabilities: Focus on scanning distance, accuracy, FOV, and echo intensity. High-performance LiDARs such as CHCNAV's AU20, which has a range of 1,450 meters and 200 scans per second, offer extended range and fast scanning, which are required for large-scale mining efficiency.
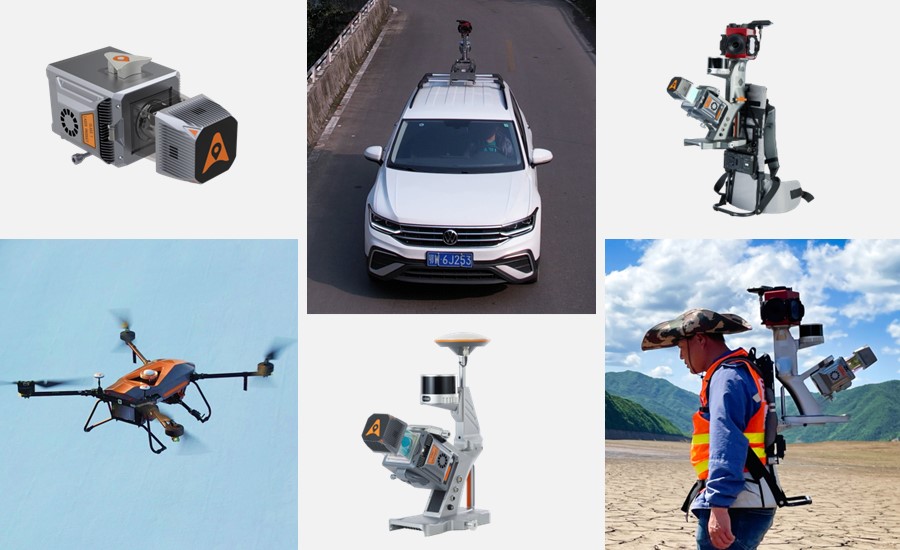

Figure 7. AlphaUni 20 multi-platform LiDAR solution for mapping.
- Cost-effectiveness: Prioritizing affordable, easy-to-use solutions with simplified deployment and reduced training requirements to balance upfront costs with long-term benefits is central to ensuring the technology delivers value for money.
THE FUTURE OF LIDAR IN OPEN-PIT MINING
The future of LiDAR in open-pit mining is promising, with affordable technologies like the CHCNAV’s AlphaUni 20 leading the way. The precision and efficiency of LiDAR systems has the potential to transform mining operations, enabling more informed decision-making and significantly improving safety protocols. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see further advances in surveying processes, resulting in even greater operational efficiencies and an increased focus on worker safety.
____
About CHC Navigation
CHC Navigation (CHCNAV) creates innovative mapping, navigation, and positioning solutions to make customers' work more efficient. CHCNAV products and solutions cover multiple industries such as geospatial, construction, agriculture, and marine. With a presence across the globe, distributors in more than 120 countries, and more than 1,700 employees, today, CHC Navigation is recognized as one of the fastest-growing companies in geomatics technologies.